Nimrod, The First Mighty One
Introduction
Nimrod, an intriguing figure mentioned in biblical scriptures, continues to spark debates and diverse interpretations. Cited in Genesis 10:8-12 as a mighty hunter and king of ancient Mesopotamia, he is recognized as the founder of cities such as Babel, Erech, Accad, and Calneh. However, his identity is shrouded in controversy, with some interpretations portraying him as a visionary leader who propelled urban and cultural development, while others view him as a tyrant who defied divine will. This ambiguity surrounding Nimrod makes him a fascinating subject for scholars and believers alike, offering insights into fundamental questions of history and faith.
By exploring the biblical narratives involving Nimrod, one can perceive the complexity of his character and the impact he had in antiquity. His association with the construction of the Tower of Babel, seen by some as an act of rebellion against God, adds an additional layer of interpretation to his story. However, others see Nimrod as a pioneer in urban expansion and the development of early civilizations, a leader who left a lasting legacy in Mesopotamia.
Historical Context of Nimrod:
During the post-Deluge period, Mesopotamia emerged as a center of innovation and human development. Favorable climate changes and the fertility of the Tigris and Euphrates river valleys provided ideal conditions for agriculture and human settlements. Yet, in this scenario, Nimrod stands out as a central figure, leading the founding of cities like Babel, Erech, Accad, and Calneh, which would become crucial points in the expansion and consolidation of the earliest urban civilizations. His role as a leader and builder in these communities underscores his influence and contribution to the early development of social and cultural organization in the region.
Examining this historical context allows us to glimpse not only Nimrod’s importance as a pioneering leader but also to understand the social and economic dynamics that drove the emergence of the first cities. The establishment of these urban centers not only provided sites for population concentration but also promoted the development of commercial activities, governance systems, and cultural interactions, thus shaping the foundations of Mesopotamian civilization and influencing future societies worldwide.
Who was Nimrod?
Nimrod is the son of Cush, who in turn is the son of Ham, one of Noah’s three sons. Thus, according to biblical narrative, Nimrod is a direct descendant of Noah and part of the post-Flood generation that spread across the land.
His occupation is described in the Bible as a “mighty hunter before the Lord,” and he is credited as the founder of various cities, as mentioned in Genesis 10:8-12. His primary occupation, as highlighted in scriptures, seems to have been that of a political leader and city builder in ancient Mesopotamia. Additionally, his skill as a hunter is also mentioned, suggesting that he may have played an active role in providing food and protecting the communities he founded. Therefore, Nimrod’s occupation appears to be a combination of a political leader, urban builder, and hunter.
The name Nimrod, also known as Nimrod or Nenrode, carries the meaning of “rebel” or “one who rebels.” This linguistic interpretation sheds intriguing light on Nimrod’s figure, suggesting an element of challenge or resistance in his personality or actions.
Biblical Interpretations:
Some view Nimrod as a symbol of rebellion and defiance against divine authority. This interpretation is based on his association with the Tower of Babel, seen by some as an arrogant attempt to defy divine decrees and reach the heavens. In this narrative, Nimrod is portrayed as a tyrannical leader who sought to elevate himself above God, thus challenging the established order and condemning his endeavor to ruin. This view suggests that Nimrod’s story serves as a reminder of the consequences of arrogance and rebellion against divine will.
However, beyond these polarized interpretations, there is a myriad of nuances and subtexts that can be explored when analyzing Nimrod’s figure in the Bible. Each perspective reveals not only different readings of the sacred scriptures but also the beliefs, values, and concerns of the communities interpreting them. By investigating these divergent interpretations, we are challenged to reflect on the nature of leadership, power, and the relationship between humanity and the divine, shedding light on fundamental questions of faith and morality.
You might also be interested in:
What is the story of the Tower of Babel?
Archaeology:
Archaeological findings related to Nimrod and the cities he founded are fundamental to our understanding of ancient Mesopotamian history. Notable archaeological sites, such as Babylon, associated with Nimrod, offer a vivid insight into the achievements and influences of these ancient civilizations. Through excavation and analysis of these sites, archaeologists identify urban structures, artifacts, and patterns of life that shed light on society and culture during Nimrod’s era.
Studying these archaeological discoveries allows us to reconstruct detailed aspects of daily life, economic activities, and social interactions at the time Nimrod lived. Furthermore, these tangible pieces of evidence help us better understand the urban development, technology, and political organization of the communities founded by Nimrod. By exploring these findings, we gain a better understanding of the accomplishments and legacy left by Nimrod and his cities in ancient Mesopotamian history.
Legends and Myths:
In addition to biblical narratives, various cultures and traditions depict Nimrod in legends and myths. The varied representations broaden our understanding of how people perceived Nimrod throughout history and his incorporation into folklore and mythology in diverse societies. Exploring these different representations helps us comprehend Nimrod’s enduring influence on the human imagination.
These divergent interpretations of Nimrod include views that portray him as a benefactor, serving the people as a hunter, protecting them from fierce animals in his region. Some suggest that, despite starting as a hunter, Nimrod attempted to expand his dominion over neighbors using force and subjugation. This view portrays Nimrod as a violent aggressor and invader, who seized others’ goods and properties to consolidate his power. The different interpretations reveal how people perceive Nimrod in varied ways across cultures, demonstrating the complexity of his figure.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Nimrod stands as an enigmatic figure, veiled in mystery and subject to varied interpretations throughout the annals of history. His prowess as a hunter, his leadership acumen, and his role as a founder of cities are pillars upon which the early fabric of human civilization was woven. Yet, within the tapestry of narratives that encompass his persona, we encounter not merely a tale of achievements, but a saga that intricately weaves the threads of human complexity and the dynamics of power in ancient times.
By delving into the depths of Nimrod’s story, we embark on a journey that compels us to confront fundamental inquiries of our shared past, the tenets of faith, and the boundless reaches of human imagination. As we unravel the layers of his legacy, we are confronted with a mirror that reflects not only the triumphs of the human spirit but also the shadows that dance upon the canvas of history.
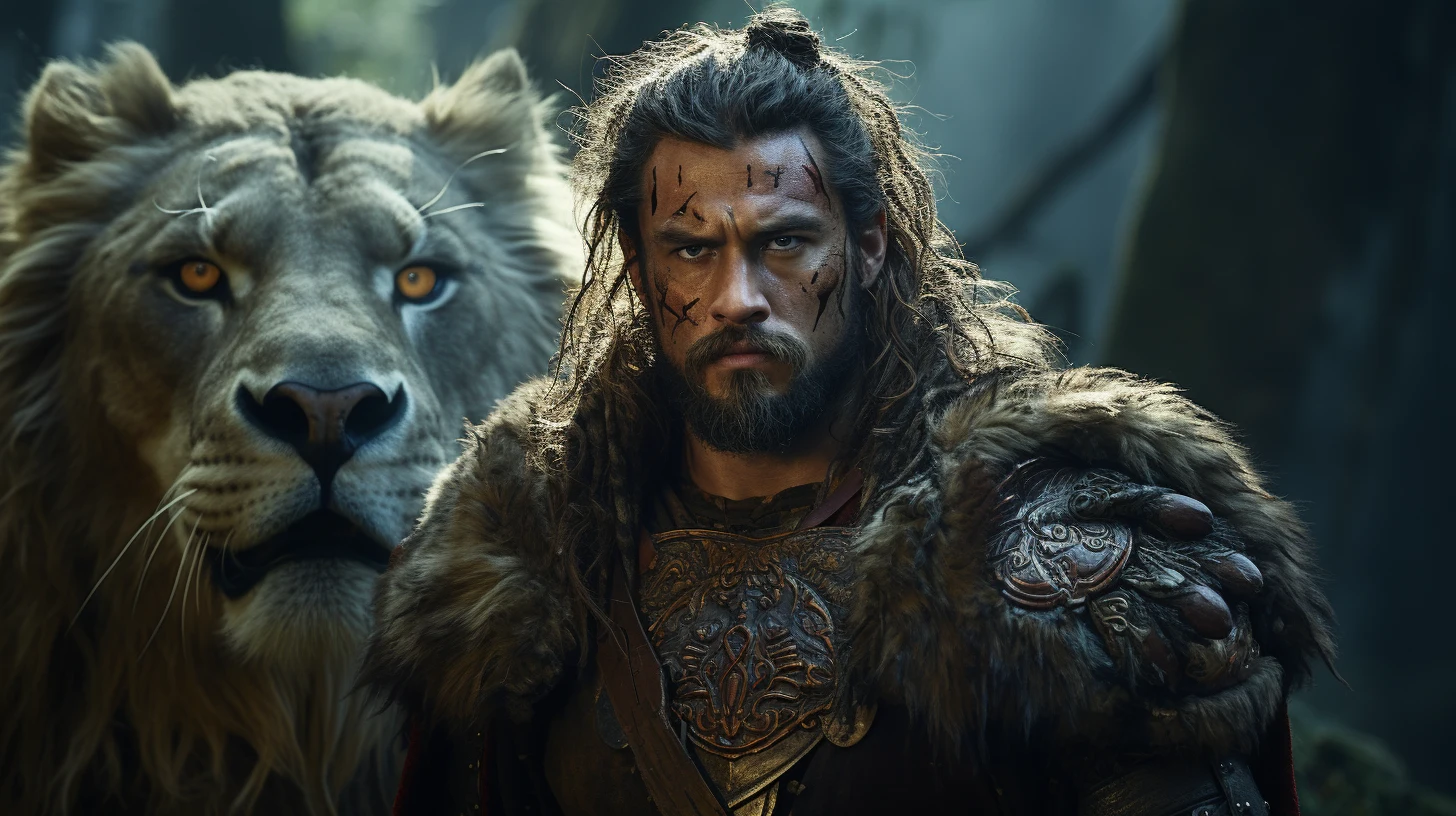 (Nimrod – Image by Luke Aquino – Midjourney)
(Nimrod – Image by Luke Aquino – Midjourney)
References:
- Bible Commentary – Old Testament, Volume 1: Genesis to Deuteronomy. CPAD, 2015.
- Beacon Bible Commentary: Genesis to Deuteronomy. RJ: CPAD, p.55
- Genesis 10:8-12